Аминокислоты
Ответы на вопросы
Консультируем и подбираем индивидуальный курс приема! Задавайте вопросы в телеграмм и ватсап
Акция! доставки по всей России безплатно!
Сайт принадлежит ИП СУДАКОВ А.Б., дистрибьютора продукции ООО "Импала биотехнологические системы"
Click to order
Ваш заказ
Total:
Оплатите заказ пластиковой картой на сайте или курьеру наличными/пластиковой картой при получении
Для оплаты заказа вы будете переадресованы на сайт платежной системы Яндекс.Касса
Ergamin complex of 18 amino acids in free form 90%, 120 capsules of 450 mg (0.016 oz) each
In stock
35
р.
44,99
р.
A complex of 18 amino acids necessary for the synthesis of enzymes.
Ergamin is a unique complex of amino acids extracted from the feedstock by deep acid hydrolysis with the release over 90% of amino acids in free form.
Ergamin is a set of free amino acids, not peptides! It gets absorbed by the body within just 20 minutes.
Ergamin is a highly purified mixture of 18 free amino acids, including 8 essential amino acids, in a ratio close to egg albumin, adopted by nutritionists as a protein standard.
Hydrolyzed amino acids are made from natural raw materials.
Ergamin is a unique complex of amino acids extracted from the feedstock by deep acid hydrolysis with the release over 90% of amino acids in free form.
Ergamin is a set of free amino acids, not peptides! It gets absorbed by the body within just 20 minutes.
Ergamin is a highly purified mixture of 18 free amino acids, including 8 essential amino acids, in a ratio close to egg albumin, adopted by nutritionists as a protein standard.
Hydrolyzed amino acids are made from natural raw materials.

Taste accent (taste): No taste
Article OZONE: 888832-1 Weight, g: 94
Shipping Weight, g: 115 White color
Type: Amino acid complex, dietary supplement, is not a medicine
Goal: Recovery, Endurance, Health and Beauty, Prevention Product
Type: Supplements, Not a Medicine
Type of dietary supplement: Amino acids
Country of manufacture: Russia
Scope: Medical nutrition, Obstetrics and gynecology, Angiology, Gastroenterology, Cardiology, Neurology, Oncology, Traumatology
Contraindications: Individual intolerance to components, pregnancy, breast-feeding. Before use, it is recommended to consult a doctor
Release form: Ergamin capsules 0,45 mg, 120 capsules
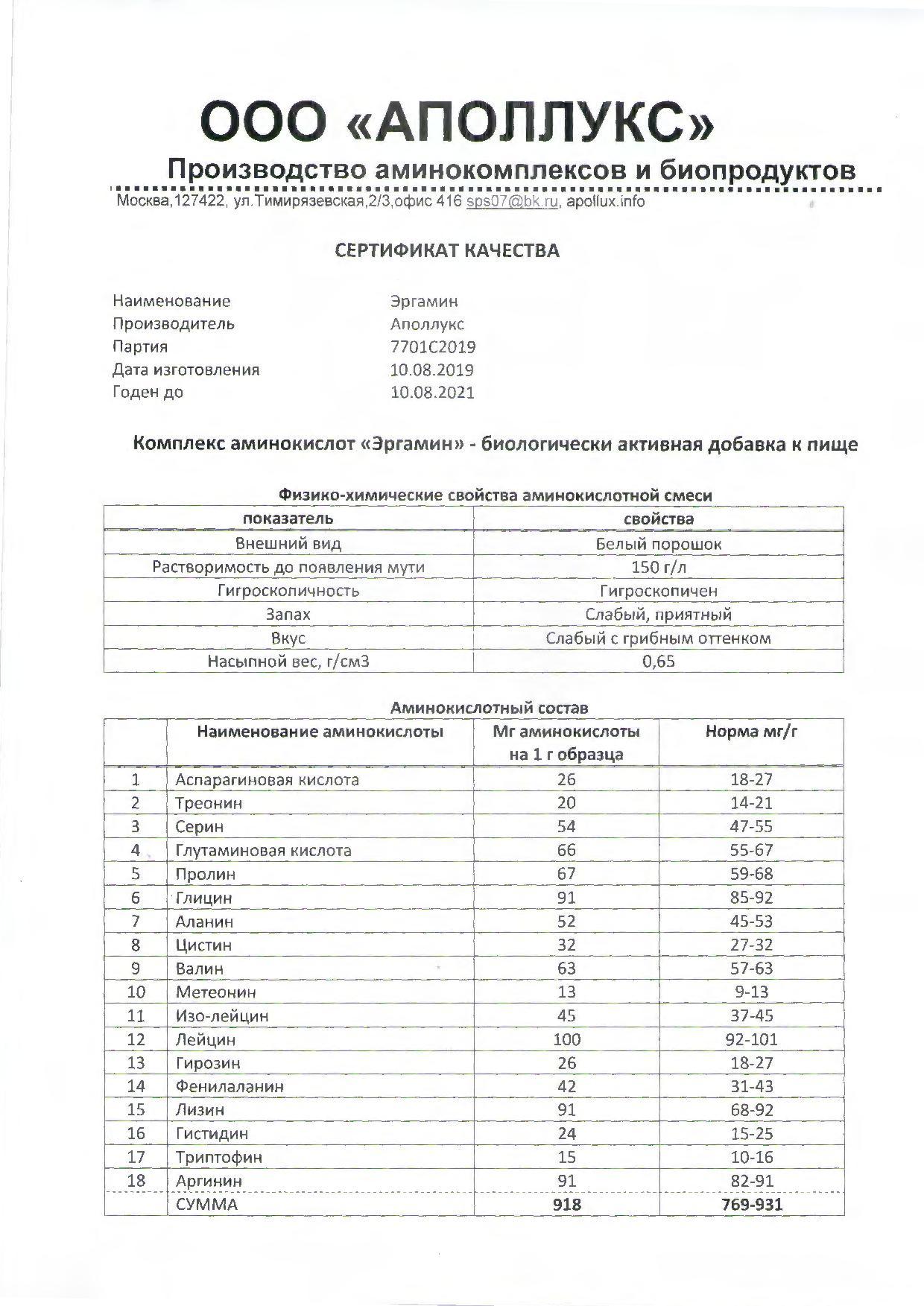
Composition Eragmine: 10 essential and 8 essential amino acids: Alanine, Arginine, Aspartic acid, Valine, Histidine, Glycine, Glutamic acid, Isoleucine, Lysine, Leucine, Methionine, Proline, Serine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan, Threonine, Phenylainlanin,
Administration way: Through the mouth
Issue order: Over-the-counter
Storage conditions: In a dry place protected from direct sunlight, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding + 25 ° С
Dosage of the active substance: 450 mg in a gelatin capsule 120 pieces per pack Goal: Recovery, Endurance, Health and Beauty, Prevention, Recovery, Muscle Gain,
Strength Energy value: 256kJ
Protein grams in 1 capsule: 0.45
Amount of packaging, pcs: 120 capsules
Article OZONE: 888832-1 Weight, g: 94
Shipping Weight, g: 115 White color
Type: Amino acid complex, dietary supplement, is not a medicine
Goal: Recovery, Endurance, Health and Beauty, Prevention Product
Type: Supplements, Not a Medicine
Type of dietary supplement: Amino acids
Country of manufacture: Russia
Scope: Medical nutrition, Obstetrics and gynecology, Angiology, Gastroenterology, Cardiology, Neurology, Oncology, Traumatology
Contraindications: Individual intolerance to components, pregnancy, breast-feeding. Before use, it is recommended to consult a doctor
Release form: Ergamin capsules 0,45 mg, 120 capsules
Composition Eragmine: 10 essential and 8 essential amino acids: Alanine, Arginine, Aspartic acid, Valine, Histidine, Glycine, Glutamic acid, Isoleucine, Lysine, Leucine, Methionine, Proline, Serine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan, Threonine, Phenylainlanin,
Administration way: Through the mouth
Issue order: Over-the-counter
Storage conditions: In a dry place protected from direct sunlight, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding + 25 ° С
Dosage of the active substance: 450 mg in a gelatin capsule 120 pieces per pack Goal: Recovery, Endurance, Health and Beauty, Prevention, Recovery, Muscle Gain,
Strength Energy value: 256kJ
Protein grams in 1 capsule: 0.45
Amount of packaging, pcs: 120 capsules
Recommended Courses

- Ergamin Properties:
- strengthens the immunity
- promotes protein formation
- reduced enzymatic deficiency
- prevents protein anemia
- improves hair and nails
- improves mental function
- helps teenagers to grow steadily
- helps to reduce body fat, as enzymes break down fat.
- Helps with both weight loss and weight gain (with extreme weight loss)
- supports brain function as amino acids help to transmit brain signals
- reduces the symptoms of diabetes
- reduces the titre of HIV infection by 1000 times
- normalizes protein metabolism
- helps to increase muscle mass
- improves metabolism
- allows weight control
- It helps for:
- protein and connective tissue deficiency: reduced hematocrit and total protein,
- reduced albumin-globulin coefficient, hemoglobin over 130
- Anemia
- Digestive problems: Meteorism, rumbling stomach, loss of appetite
- Bowel problems: constipation or irritable bowel syndrome
- Fatigue or lack of energy
- weak immune system
- chronic stress
- overweight or underweight

Who needs Ergamin:
 Healthy lifestyle - strength training and fast recovery
Healthy lifestyle - strength training and fast recovery Breastfeeding mothers - to restore blood protein levels, strengthen immunity and vitality
Breastfeeding mothers - to restore blood protein levels, strengthen immunity and vitality People who are prone to depression - to balance moods and improve mental state
People who are prone to depression - to balance moods and improve mental state Older people - to slow aging processes and support the body
Older people - to slow aging processes and support the body Women after menopause
Women after menopause- Athletes - for muscle building, reduced recovery time and improved endurance

THE ROLE OF ERGAMINE IN HIGH PHYSICAL AND MENTAL STRESS
If you lead an active lifestyle, the need for Wargaming as a complex of amino acids increases dramatically for you. Protein synthesis is a basis for fat burning and weight gain. It depends directly on the amount of the essential amino acid lysine, which can be obtained from Pergamon.
Ergamin plays two strategic roles for athletes: muscle growth and muscle regeneration after heavy and regular training sessions and exercises. Ergamine also strengthens the joint and ligamentous apparatus, which helps to prevent injuries in the future.
It should be noted that arginine amino acid can enhance the effect of the ergamine course when taken together.
Ergamin plays two strategic roles for athletes: muscle growth and muscle regeneration after heavy and regular training sessions and exercises. Ergamine also strengthens the joint and ligamentous apparatus, which helps to prevent injuries in the future.
It should be noted that arginine amino acid can enhance the effect of the ergamine course when taken together.

Go to our YouTube channel and even learn
more about amino acids and their benefits
more about amino acids and their benefits
Do you have questions about amino acids and their positive effects?
Give us your ideas and we will record new videos that you are curious about.
Give us your ideas and we will record new videos that you are curious about.
Ergamin = perfect PROTEIN. Strengthens the immune system! Slows down aging! How? Watch and learn
Ergamin + lysine scientific research has been running for 25 years, biotechnologist Ter-Sargsyan
Arginine and lysine help restore reproductive health. Stroke prevention and to strengthen the immune system!
Why do we lack protein and where do we get it? Why do we need amino acids? Biotechnologist Eric Ter-Sargsyan
Pergamon + collagen it is recommended for: ligaments, blood vessels, skin, heart, biotechnologist Eric Ter-Sargsyan
Arginin and lysine help restore reproductive health. Stroke prevention and to strengthen the immune system!
Subscribe to our YouTube channel to learn more about
other amino acid supplements and their benefits
other amino acid supplements and their benefits
- Igor Rubinovich"It hasn't even been two weeks and I feel great already".
It's not even been two weeks, and I feel great already. The last time I experienced such a boost, was when I tried creatine for the first time. And it was almost 30 years ago. Now I recover with a bang. And overall, My Health has improved. I think it was L-lysine amino complex that contributed to this. - Arginine + lysine: 30 years of intensive training, healthy lifestyle, boxing, athletics
-
Eugene, Moscow, 56: energy, rapid recovery, review - Nika: ergamine classes, no knee pain, great hair and nails

Types and functions of protein in the body:
There is a conditional division of proteins into products and organisms into subspecies::
Protein functions:
catalytic - helps to accelerate biochemical reactions (synthesis or cleavage of molecules, etc.).). This function is provided by special proteins - enzymes contained in foods and produced by the body.
Energy - is responsible for the energy production during the degradation of proteins and is activated only when other energy sources (fats and carbohydrates) are consumed.
Protection - protects body at the physical level (blood clotting, maintaining the normal state of connective tissue and epidermis), chemical (neutralization of toxins) and immune defense (forms a reaction to the effects of pathogenic microorganisms or damage, neutralizes viruses and bacteria, etc.).
structural (construction) - manifests itself in the formation of cells and a change in their shape.
Regulatory - regulates the activity of a number of proteins, promoting cell structures in a cycle and other processes (e.g. stimulating the formation of fats from carbohydrates, regulating blood sugar levels, etc.).).
signal - is responsible for the transmission of intercellular and interstitial signals.
transport - provides Transport of small molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc.) within the body as well as from cells into space and vice versa.
reserve - forms a stock of certain proteins that serve as energy sources or amino acid sources.
receptor - used to receive signals (mechanical effects, chemicals, light, etc.) and transmit them to other cellular components.
Movement capability - provides the processes of movement in the body (intracellular transport, movement of cells, muscle contraction, etc.).
- Peptides (polypeptides) protein compounds of 2 to several ten residual amino acids in length, which are formed by the condensation of amino acids.
- Free (Unbound) amino acids are completely cleaved protein molecules, which are isolated substances or complex compounds.
- Proteins are substances with a higher degree of polymerization. A separate class of proteins are enzymes that are biological catalysts. These substances contribute to the multiple acceleration of biochemical reactions in the body.
Protein functions:
catalytic - helps to accelerate biochemical reactions (synthesis or cleavage of molecules, etc.).). This function is provided by special proteins - enzymes contained in foods and produced by the body.
Energy - is responsible for the energy production during the degradation of proteins and is activated only when other energy sources (fats and carbohydrates) are consumed.
Protection - protects body at the physical level (blood clotting, maintaining the normal state of connective tissue and epidermis), chemical (neutralization of toxins) and immune defense (forms a reaction to the effects of pathogenic microorganisms or damage, neutralizes viruses and bacteria, etc.).
structural (construction) - manifests itself in the formation of cells and a change in their shape.
Regulatory - regulates the activity of a number of proteins, promoting cell structures in a cycle and other processes (e.g. stimulating the formation of fats from carbohydrates, regulating blood sugar levels, etc.).).
signal - is responsible for the transmission of intercellular and interstitial signals.
transport - provides Transport of small molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc.) within the body as well as from cells into space and vice versa.
reserve - forms a stock of certain proteins that serve as energy sources or amino acid sources.
receptor - used to receive signals (mechanical effects, chemicals, light, etc.) and transmit them to other cellular components.
Movement capability - provides the processes of movement in the body (intracellular transport, movement of cells, muscle contraction, etc.).

USE
As a biologically active dietary supplement, it is an additional source of pure protein. Consists of 10 non-essential and 8 essential amino acids: alanine, arginine, aspartic acid, valine, histidine, glycine, glutamic acid, isoleucine, lysine, leucine, methionine, Proline, serine, tyrosine, tryptophan, threonine, phenylalanine, CysteinAs a biologically active food supplement, it is an additional source of pure protein. Consists of 10 nonessential and 8 essential amino acids: alanine, arginine, aspartic acid, valine, histidine, glycine, glutamic acid, isoleucine, lysine, leucine, methionine, proline, serine, tyrosine, tryptophan, threonine, phenylalanine, cysteine

Course is 3 packs.Course is 3 packs.
For Adults::
Break in three doses during the day, take with food or after meals.
For Children
Break in three doses during the day, take with food or after meals.
Take with a glass of water.
For Adults::
Break in three doses during the day, take with food or after meals.
- for strong immune system-3 capsules 3 times a day;
- Weight loss or control of appetite and weight: up to 20 capsules throughout the day;
- Recovery after strength training: up to 5 capsules before training and up to 10 capsules then;
- Recovery from a stroke: course of at least 2 months, during the day: ergamine 8 capsules + Collagenite 10 ml (2 tsp) + lysine 8 capsules
For Children
Break in three doses during the day, take with food or after meals.
- 3 years old - 3 capsules;
- 5 years old - 4 capsules;
- 10 years old - 5 capsules;
- 12 years and older-6 capsules;
Take with a glass of water.
The person who stood at the origins of Soviet biotechnology ,
is responsible for production and quality control
is responsible for production and quality control

Eric Ter-Sarkissjan, Promotion in Chemie
Biotechnologist with 50 years of experience
55 patents for inventions and copyrights, technologies
More than 250 scientific publications
Head of the radiobiological department, Institute of atomic energy of I. V. Kurchatov
Improvement of production technology for anti-gangrene antibiotic Polymyxin
2016 - world-AIDS-conference, organization, presentation
Biotechnologist with 50 years of experience
55 patents for inventions and copyrights, technologies
More than 250 scientific publications
Head of the radiobiological department, Institute of atomic energy of I. V. Kurchatov
Improvement of production technology for anti-gangrene antibiotic Polymyxin
2016 - world-AIDS-conference, organization, presentation
Patents and certificates
Patent for an invention in 1968. Process for the production of L-lysine, E. M. Ter-Sargsyan, co-author
Download the patent ...
Patent for an invention, in 1988. The method of isolation of lysine, E. M. Ter-Sargsyan, co-author
Download the patent ...
Patent for invention in 2008. A method for the production of an amino acid mixture of a protein hydrolysate, E. M. Ter-Sargsyan.
Download the patent ...
Patent for an invention, 2017. The method for the production of fully-hydrolyzed collagen, E. M. Ter-Sargsyan author
Download the patent ...
Download the patent ...
Patent for an invention, in 1988. The method of isolation of lysine, E. M. Ter-Sargsyan, co-author
Download the patent ...
Patent for invention in 2008. A method for the production of an amino acid mixture of a protein hydrolysate, E. M. Ter-Sargsyan.
Download the patent ...
Patent for an invention, 2017. The method for the production of fully-hydrolyzed collagen, E. M. Ter-Sargsyan author
Download the patent ...
Registration documents: Ergamin (certificate of state registration); L-lysine (Declaration of the customs Union); Collagenit (certificate of conformity). All supplements are registered in all EU countries (Ministry of health of the Czech Republic)
There are safety data sheets (SDS) for each batch.
A safe dosage has not been determined because the end product is made from organic raw materials and excess amino acids simply leave the body naturally. The usual dosage is 6 capsules per day with meals. Consult your doctor before use.
The Production Technology. Ergamine is a highly purified mixture of 18 free amino acids in the ratio near the egg albumin, which is adopted by nutritionists as a protein standard. Meat and poultry production waste containing keratin protein is used as raw materials. These are horned flour (97% keratin), pig bristles (75% keratin), feather meal (72% keratin). The manufacturing process of a supplement complex includes: acid hydrolysis of keratin; sorption on anionite (anion exchange resin), clarification of the resulting amino acid solution; elution of amino acids from cation exchangers; sterilize the ultrafiltration of an amino acid solution and spray or freeze-dry the drug. The resulting product is a white, loose, slightly hygroscopic odorless powder with a weak mushroom taste that is well soluble in water. The powder is slightly encapsulated. The L-lysine production technology is similar. Feed L-lysine is used as raw materials. The Collagenite technology is identical to ergamine. Raw material for Collagenes is a cleavage of cattle skins. No additives such as magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide, etc., are used in production.
Yes, you can. Take 6 capsules per day for 60 days.
As young as 6 months. The contents of the capsule can be mixed with soup, juice or porridge.
Yes, you can. For a two-year-old you should give him 2 capsules per day. One in the morning, one in the afternoon during or after meals.
3 years old - 3 capsules
5 years old - 4 capsules
10 years old - 5 capsules
12 and older - 6 capsules
Younger than 3 years - dosage is calculated individually
Take 3 times a day during or after meals.
3 years old - 3 capsules
5 years old - 4 capsules
10 years old - 5 capsules
12 and older - 6 capsules
Younger than 3 years - dosage is calculated individually
Take 3 times a day during or after meals.
In case of gout, you should take antibiotics. Gout is a disease that begins and progresses as a result of metabolic disorders. The first thing the Argument does is it fixes metabolic processes.
The best option for you taking Ertgaming is 6-8 capsules per day + 10 ml (2 tbsp) collagen it + 6-8 capsules of lysine per day. Follow this Regime for at least 2 months.

Andere Produkte
Click to order
Your Order
Total:
Pay for your order with a plastic card on the website
Thank you for ordering, our staff will contact you within 15 minutes and provide delivery details